[wp_campaign_1]
Iran is only a matter of months from being able to create a nuclear weapon, according to experts.
President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad, 54, has long been pushing his country’s nuclear capabilities, and at the current rate of uranium enrichment the first bomb could be eight weeks away.
Gregory S. Jones, from RAND, published a report this week explaining the severity of the situation and to confirm the fears expressed by a United Nations watchdog.
In spite of a number of set backs, says the researcher, the Iranian regime is back on track with their nuclear programme – and there is very little American, or the U.N. can do about it.
Jones based his report on recent findings by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) – their report was published two weeks ago.
Manufacturing the bomb will take about two months, Jones believes – as constructing a nuclear warhead is a complicated process.
In order to halt the process, Jones comments, forces will have to deploy ground forces – airstrikes will no longer be sufficient.
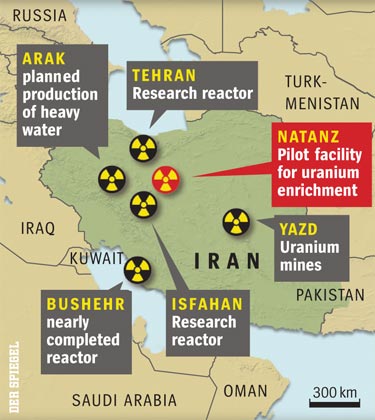
He believes that Tehran, the Iranian capital, has produced 38.3kg of uranium enriched at 19.7 per cent.
If its centrifuges continue to work at the current capacity, it will take around two months for the Iranian regime to produce the 20 kg of uranium enriched to 90 per cent required for the production of a nuclear warhead.
Meanwhile Yukiya Amano, director general of the 35-nation IAEA, made clear in a speech his growing frustration at the Islamic state’s failure to answer agency queries about its nuclear programme.
His remarks are likely to be welcomed by Western powers as a sign that he is gradually ratcheting up the pressure on Iran – but the hope is that he is not too late.
The U.S. and its allies accuse Iran of seeking to develop an atomic weapons capability.

The Iranian nuclear scientist who defected to the United States is thought to have worked on the Iran nuclear program at this suspected uranium-enrichment facility near Qom, Iran.
Iran rejects the accusation, saying its nuclear programme is aimed at generating electricity so that it can export more of its oil and gas.
For several years, the IAEA has been investigating Western intelligence reports indicating Iran has coordinated efforts to process uranium, test explosives at high altitude and revamp a ballistic missile cone so it can take a nuclear warhead.
Western diplomats believe Amano is in effect warning Tehran to co-operate or face a possible assessment by the IAEA on the likelihood it has conducted nuclear activity with possible military aspects.
Such an assessment could lend weight to any renewed Western push to tighten sanctions on the major oil producer.
Amano said the U.N. agency had received ‘further information related to possible past or current undisclosed nuclear-related activities that seem to point to the existence of possible military dimensions to Iran’s nuclear programme’.
The Japanese later told a news conference, without disclosing the source of the information: ‘The activities in Iran related to the possible military dimension seem to have been continued until quite recently.’
Iran’s refusal to halt uranium enrichment, activity which can have both civilian and military uses, has drawn four rounds of U.N. sanctions since 2006.
Amano said he had written last month to the head of Iran’s Atomic Energy Organisation, Fereydoun Abbasi-Davani, to reiterate ‘the agency’s concerns about the existence of possible military dimensions’.
He had also asked for Iran to ‘provide prompt access’ to locations, equipment, documentation and officials to help resolve the agency’s queries.
Abbasi-Davani replied and said U.N. sanctions resolutions against his country were ‘illegal and unacceptable’.
Iran was ‘not providing the necessary cooperation to enable the agency to provide credible assurance about the absence of undeclared nuclear material and activities in Iran’, Amano said.
‘I urge Iran to take steps towards the full implementation of all relevant obligations in order to establish international confidence in the exclusively peaceful nature of its nuclear programme,’ he added.
[wp_campaign_1]